What Are Tympanograms?
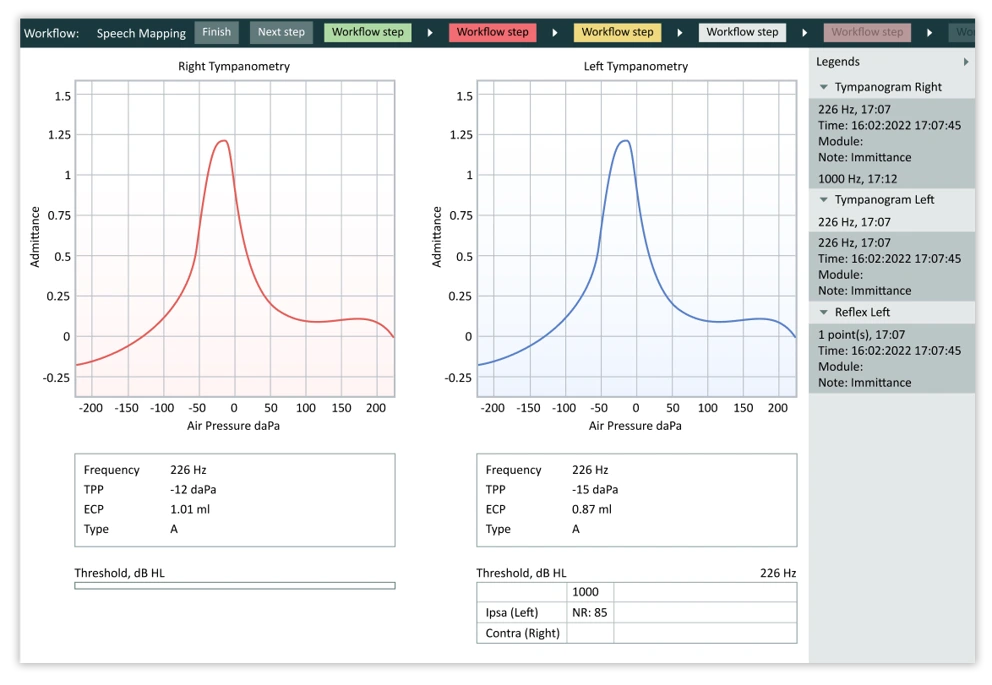
Tympanograms are a graphical representation of the results of a tympanometry test. Tympanometry involves placing a small probe in the ear canal and changing the pressure within the ear canal. At a certain pressure, the sound transmission through the middle ear will peak. The results are plotted on a graph called a tympanogram. This graph contains information about ear canal volume, middle ear acoustical compliance, and middle ear pressure. These values, or the shape of the tympanogram itself can indicate different pathologies and aid in differential diagnosis.
Common Middle Ear Pathologies
While the number of pathologies involving the middle and outer ear are vast, some are more common than others. Below, we will discuss a few of the most common diagnoses and their corresponding tympanometric results.
1. Otitis Media With or Without Effusion
Otitis media is an infection in the middle ear that can cause a build-up of fluid in the middle ear space. When fluid is present, the disorder is referred to as otitis media with effusion. In short, otitis media is caused by eustachian tube dysfunction as the eustachian tube is responsible for drainage and equalizing pressure in the middle ear. Eustachian tube dysfunction, and subsequently otitis media, are often associated with an existing cold or respiratory infection and most commonly occur in children.
In otitis media without effusion or fluid, the eustachian tube has failed to equalize pressure in the middle ear resulting in negative pressure and often a retracted tympanic membrane. Tympanometry can detect this negative pressure. A tympanogram in this case will present with a peak at a negative pressure point. Ear canal volume and compliance or static admittance will likely be normal.
With middle ear effusion, or a build-up of fluid in the middle ear, a distinct tympanogram will result. This built-up fluid that results from a non-functional eustachian tube, will prevent the tympanic membrane from moving entirely. The resulting tympanogram will appear completely flat. Ear canal volume will likely be normal, but no tympanic membrane movement or middle ear pressure will be detected
2. Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis refers to a condition that involves an abnormal hardening of the stapes, a small bone in the middle ear. This stiffening of the bone prevents sound transmission from the middle to the inner ear. This disorder is often progressive and can present with hearing loss of varying severities, tinnitus, and even dizziness.
Most often, an individual with otosclerosis will present with normal ear canal volume and normal middle ear pressure, but with low compliance. In other words, the tympanogram will appear shallow.
While otosclerosis can be detected on tympanometry, individuals with this disorder can present with a normal tympanogram. Additionally, some normal individuals can present with the tympanogram shape associated with otosclerosis. As a result, it is important to assess tympanometric results with patient history, audiometry, and other measures.
3. Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Tympanic membrane perforation, or a hole in the ear drum, can be a result of a myriad of things such as untreated otitis media or trauma. Individuals with a tympanic membrane perforation may present with hearing loss, ear pain, tinnitus, aural fullness, and even dizziness. Tympanometry is an important tool in the diagnosis of tympanic membrane perforation as some may be so small they are not visible to the naked eye.
The tympanogram that results from tympanic membrane perforation will look similar to that of middle ear effusion as the perforation will prevent ear drum movement and thus the tracing will be completely flat. In contrast to a fluid filled ear, however, the ear canal volume in an ear with a perforation will be abnormally large.
4. Ossicular Chain Discontinuity
The ossicle chain is a series of three small bones in the middle ear. These bones help transmit sound from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear. At times, trauma, like head injury, can cause the ossicular chain to dislocate or detach from one another. Diseases like cholesteatoma or a growth in the ear can also cause ossicular chain discontinuity by eroding these three bones.
Individuals with this disorder will present with similar symptomology as the aforementioned pathologies – hearing loss, tinnitus, aural fullness, and/or dizziness. A tympanogram reflecting this pathology will present with normal ear canal volume and pressure but high compliance. In short, the tympanogram peak will appear higher than normal as the middle ear system is hypermobile.
Like with otosclerosis, it’s important to note that this tympanogram shape can present in individuals without ossicular chain discontinuity and thus patient history, audiometry, and other measures should be considered.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for these conditions varies greatly not only between the diagnoses, but with disease severity. Treatment can include medications like antibiotics, avoiding triggers like allergens, watching and waiting, the use of hearing aids, and even surgery. Regardless of treatment type, tympanometry can be used to monitor disease progress. These results can help guide future management and treatment plans.
Tympanograms are an essential tool in the diagnosis and management of middle ear disorders such as otitis media and otosclerosis. The graphical representation of the results of a tympanometry test can provide valuable information about the condition of the middle ear. Tympanometry can also be used to monitor the progress of treatment for these conditions.
Measure Tympanometer
Portable Diagnostic Tympanometer
Portable Diagnostic Tympanometer
In order for tympanometry to be useful and effective, a reliable tympanometer is necessary. The Measure Tympanometer provides clinicians with reliable results all while providing an intuitive and user-friendly interface.

Other Blogs You Might Enjoy:

Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Symptoms, Causes, and Testing Methods
The eustachian tube is a crucial part of the middle ear system. Testing eustachian tube function is essential in obtaining a complete patient picture in the presence of middle ear related symptoms.

Are Real Ear Measurements Necessary?
Real Ear Measurements (REM) – also called Probe Microphone Measurements (PMM) – are considered the gold standard in hearing aid fitting and verification, allowing audiologists to determine whether a hearing aid user is receiving the precise level of amplification needed at every frequency to maximize their hearing. This blog explains how REM can improve customers’ hearing, as well as drive better business outcomes and serve as a key differentiator for hearing clinics.

Distinguishing Cochlear from Retrocochlear Pathologies: A Review of Test Options
Cochlear and retrocochlear pathologies can both result in hearing loss but the underlying cause, site of lesion, and patient presentation differ between the two. Distinguishing between these two categories of pathology is important when considering treatment options and prognosis. When interpreting an audiogram alone, it is nearly impossible to determine whether a hearing loss is a result of a cochlear or retrocochlear pathology. This is where advanced testing techniques, like the SISI, acoustic reflexes, and acoustic reflex decay come into play.
Don't Miss Out On the Latest Insights On Audiology
Sign up today to receive exciting updates, tips, and the latest newsletters from Auditdata.