Create The Optimal Testing Environment
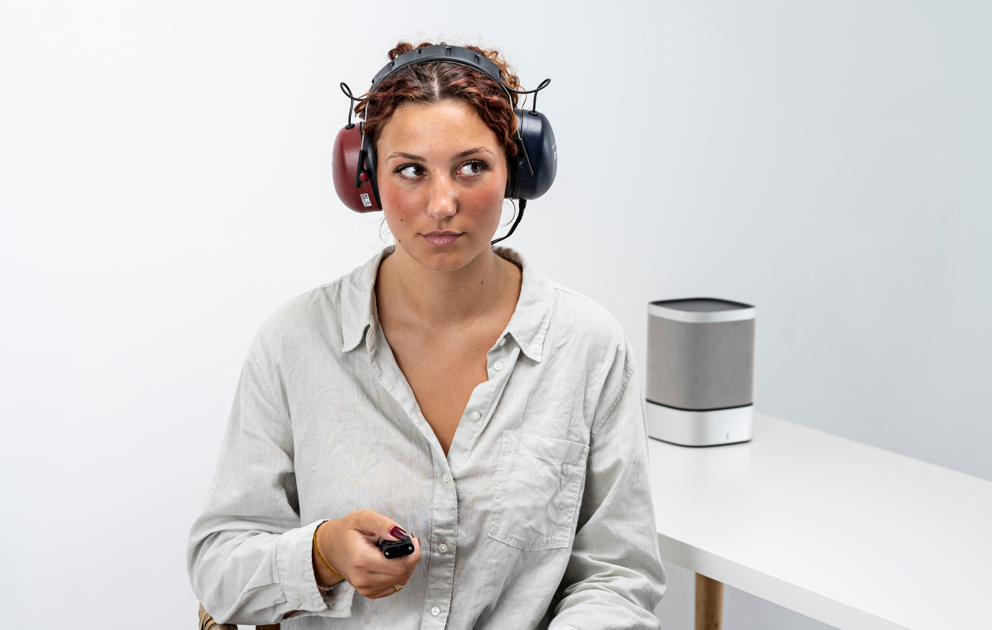

Creating an optimal testing environment is crucial for accurate audiometric assessments. Background noise, ambient conditions, and distractions can impact results significantly. Conduct assessments in soundproof rooms or environments designed to minimize external influences. Additionally, instruct patients to report discomfort or difficulties during the test to improve overall accuracy.
If a soundproof booth isn’t available, for example when conducting pure tone audiometry in a school or nursing home environment, try to select as quiet a location as possible. Providers should also consider room acoustics, for example, the size of the room and the presence, or lack of, soft materials that help minimize reverberation.
Some audiometers offer the possibility of measuring and monitoring the background noise level. This is a valuable feature to ensure the quality of the measured hearing thresholds.
Prepare Patient Properly
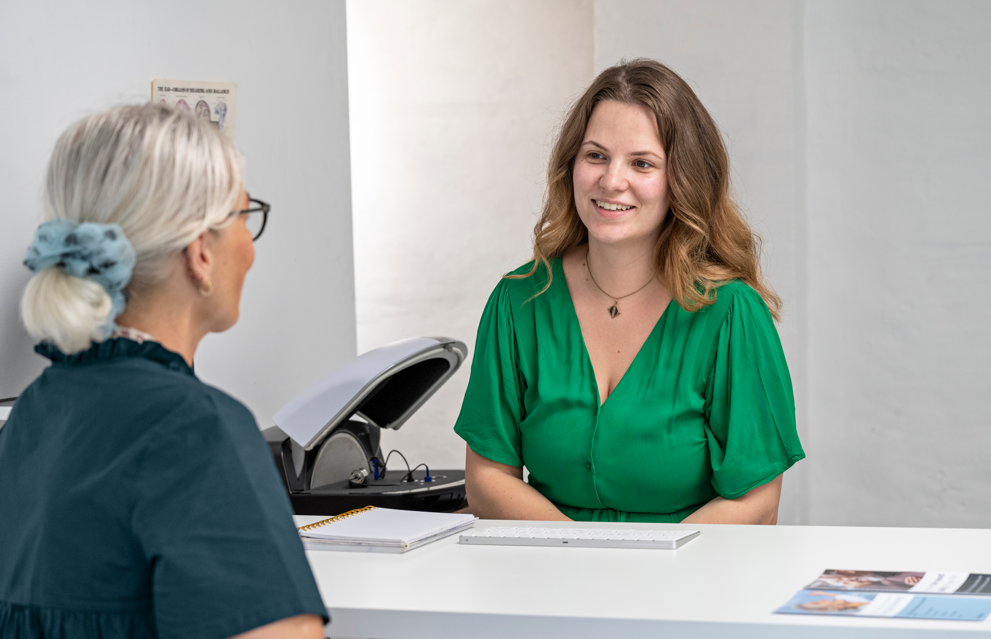

Educate patients about the audiometric assessment procedure and provide clear instructions. If a language barrier is present, ensure your instructions are translated into the language the patient is most comfortable with by a reputable source. Speech audiometry should also be conducted in the patient’s native language if possible.
Emphasize the importance of honesty during the test and encourage them to communicate any uncertainties. A relaxed and informed patient is more likely to provide accurate responses, leading to a more reliable audiogram. Selecting the appropriate method of testing is also crucial.
While most individuals over the age of 6 or 7 can simply respond to tones by pressing a button or raising their hand, outliers may exist. For young children, and other individuals with comorbid disabilities, audiometric procedures like video reinforcment audiometry (VRA) or conditioned play audiometry (CPA).
Threshold Determination
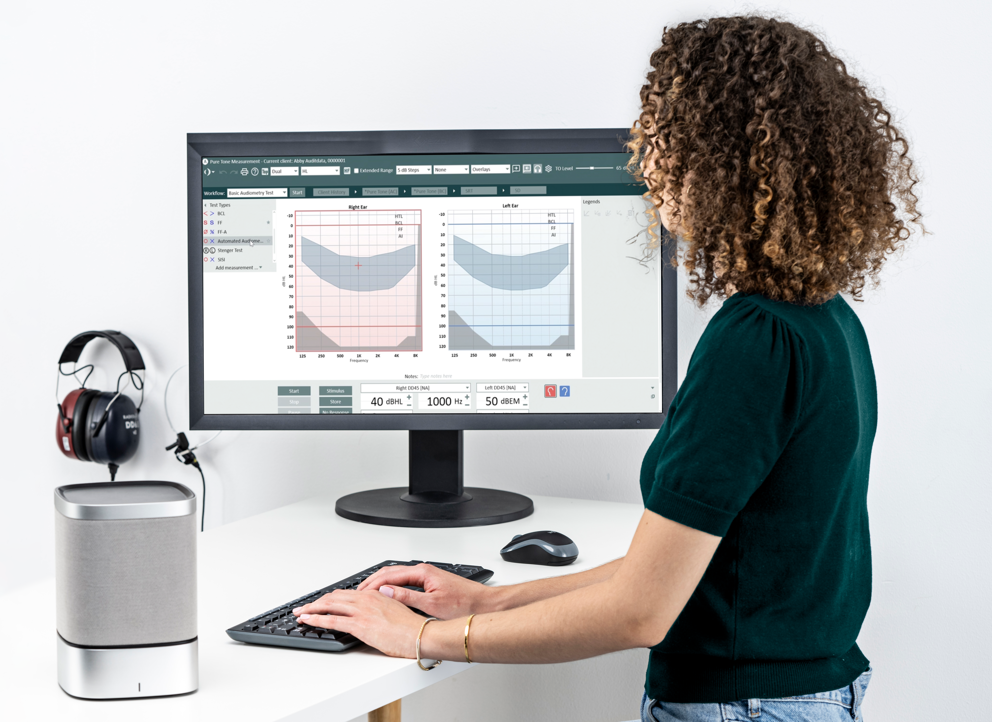
Establishing hearing thresholds requires a systematic and precise approach. Employ reliable threshold determination methods, such as the Hughson-Westlake method, to ensure accuracy. Conduct thorough testing across various frequencies to identify any potential hearing deficiencies comprehensively. Providers should consider things like patterned responses to ensure results are accurate.
It's essential to consider the broader scope of comprehensive audiology assessments. This thorough evaluation includes various tests such as pure-tone audiometry, speech audiometry, tympanometry, and otoacoustic emissions (OAEs), each contributing valuable information about the patient's auditory health.
Masking plays a pivotal role in audiological assessments by ensuring that the results obtained are accurate and consistent especially in situations where one ear may have significantly better hearing than the other.
Masking is employed to prevent the better ear from influencing the results of the ear being tested. By presenting masking noise to the non-test ear, audiologists can isolate the response of the ear under examination, providing a more precise evaluation of its auditory thresholds.
Masking is an essential tool that enhances the reliability of hearing tests, enabling healthcare professionals to tailor interventions and recommendations based on a thorough and accurate understanding of an individual's hearing capabilities.
Speech Testing
Incorporate speech audiometry alongside pure tone testing to assess the patient's ability to understand spoken words. This provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the individual's overall hearing function, enabling a more accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Speech audiometry helps not only to validate pure-tone results but also provides insight into an individual’s ability to understand speech.
Additionally, as most individuals have difficulty understanding speech in noise, speech-in-noise testing is a critical step in a complete hearing assessment.
Record Keeping and Documentation
Maintain detailed and organized records of audiometric assessments. Accurate documentation facilitates easy tracking of a patient's hearing history and aids in the identification of patterns or changes over time. This documentation is invaluable for healthcare providers and audiologists, ensuring consistency in patient care.
Auditdata Manage
Retrieve Historical Patient Notes with Ease
With Manage, audiologists can quickly and efficiently find the information they need without having to search through multiple documents or records manually. This saves time and ensures that the most accurate information is used when treating patients, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Continue Professional Development

The field of audiology is dynamic, with advancements in technology and methodologies. Audiologists and healthcare professionals should engage in continuous learning and stay updated on the latest developments. Attend workshops, conferences, and training sessions to enhance skills and stay abreast of best practices in audiometry.
Optimizing audiometric assessments involves a combination of precise equipment calibration, environmental considerations, patient preparation, and adherence to standardized testing methodologies. By implementing these best practices, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy and consistency of audiometric results, ultimately improving the quality of care for individuals with hearing disorders.
Measure E-learning
Explore Our E-Learning Course on Advanced Audiometry in the Measure Software
We are delighted to present this comprehensive e-learning course aimed at providing an in-depth understanding of the additional assessments available in the audiometry module within Measure, including the SISI, TEN, Weber, and Stenger tests.

Calibration And Equipment Maintenance
To achieve precise results, regular calibration of audiometric equipment is paramount. Ensure that audiometers, headphones, and transducers are well-maintained and meet the necessary standards. Regular checks and calibrations guarantee that the equipment functions accurately, providing reliable data for diagnostic purposes.
With the Measure software, loudspeakers can be calibrated using the Real Ear Measurement reference microphone. This eliminates the need to schedule lengthy calibration appointments and ensures testing completed with loudspeakers is as accurate and reliable as possible.
Say Goodbye to Equipment Downtime!
Auditdata empowers providers by facilitating the seamless exchange of malfunctioning transducers, ensuring uninterrupted care. Replacement transducers are dispatched to the clinic ahead of the return of malfunctioning units with our SWAP Service.
Other Blogs You Might Enjoy:
The History of Audiometry and The Evolution of Audiometers
In short, audiometry is the study of the sensitivity of an individual’s hearing that has been performed for more than 150 years! An audiometer is a tool used to ascertain this information. This blog elaborates on the history of audiometry, and the evolution of audiometers as these are closely intertwined with not only each other but the advancement of the field of audiology as a whole.

Are Real Ear Measurements Necessary?
Real Ear Measurements (REM) – also called Probe Microphone Measurements (PMM) – are considered the gold standard in hearing aid fitting and verification, allowing audiologists to determine whether a hearing aid user is receiving the precise level of amplification needed at every frequency to maximize their hearing. This blog explains how REM can improve customers’ hearing, as well as drive better business outcomes and serve as a key differentiator for hearing clinics.

Cochlear Dead Regions: How To Assess With TEN Testing And Manage With Frequency Lowering
Hearing loss is a common problem, affecting millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, noise exposure, genetics, and illness. In some cases, individuals with hearing loss may experience cochlear dead regions, which can make it difficult to understand speech and other sounds. In this article, we will discuss cochlear dead regions, how to identify them with TEN testing, and managing dead regions with frequency lowering in hearing aids.
Don't Miss Out On the Latest Insights On Audiology
Sign up today to receive exciting updates, tips, and the latest newsletters from Auditdata.